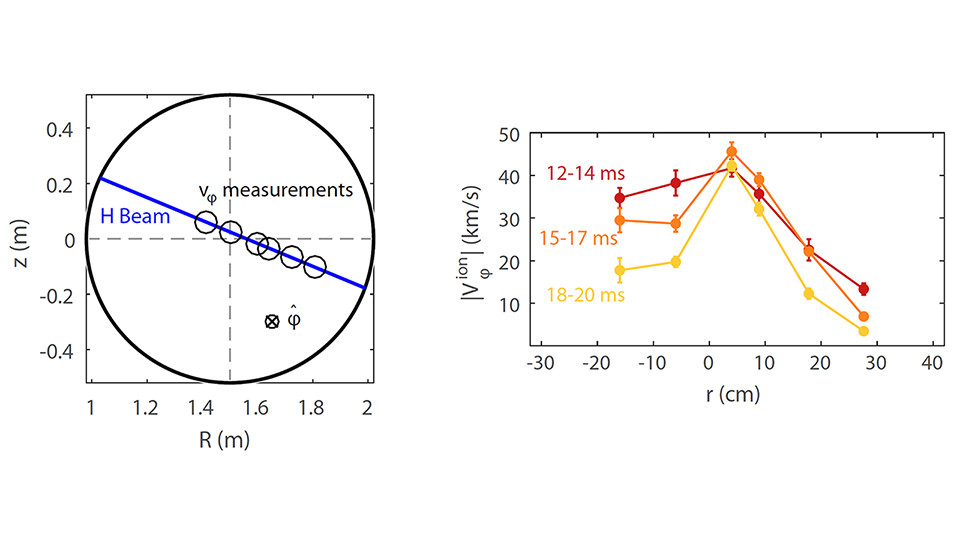
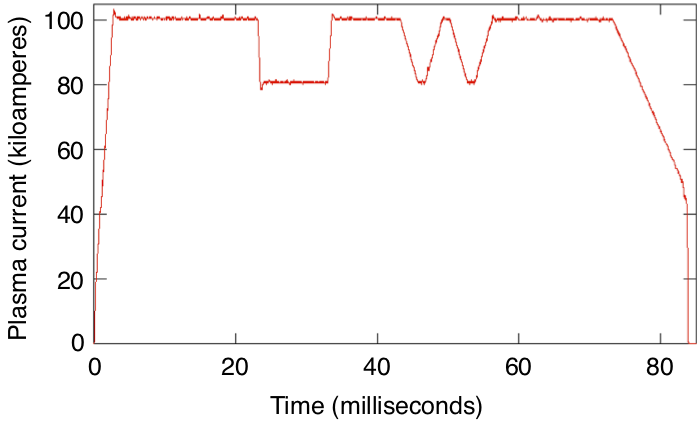
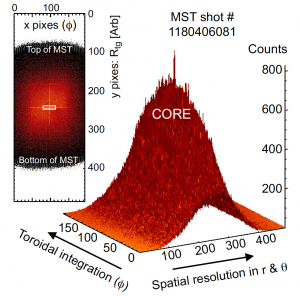
Two projects on MST have been selected for invited talks at the High-Temperature Plasma Diagnostics conference in May 2020:
Patrick VanMeter, University of Wisconsin–Madison
Robust analysis of space-, time-, and energy-resolved soft x-ray measurements of magnetically confined fusion plasmas
A new concept for a multi-energy soft x-ray (ME-SXR) diagnostic is being developed by a PPPL/WiPPL collaboration on the MST facility. This diagnostic is based on a custom calibration of a solid-state detector consisting of a 2D array of ∼100,000 pixels. The lower photon absorption cutoff energy can be independently set for each pixel. Results from MST illustrate how the detector can be used to study the evolution of thermal and impurity density profiles. Similar diagnostics will soon be installed on NSTX-U and WEST, including a hard x-ray variant based on a CdTe sensor. This diagnostic may eventually be applied to ITER, where small, non-perturbative diagnostics will be necessary for routine steady state operation.
Megan Eckart, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
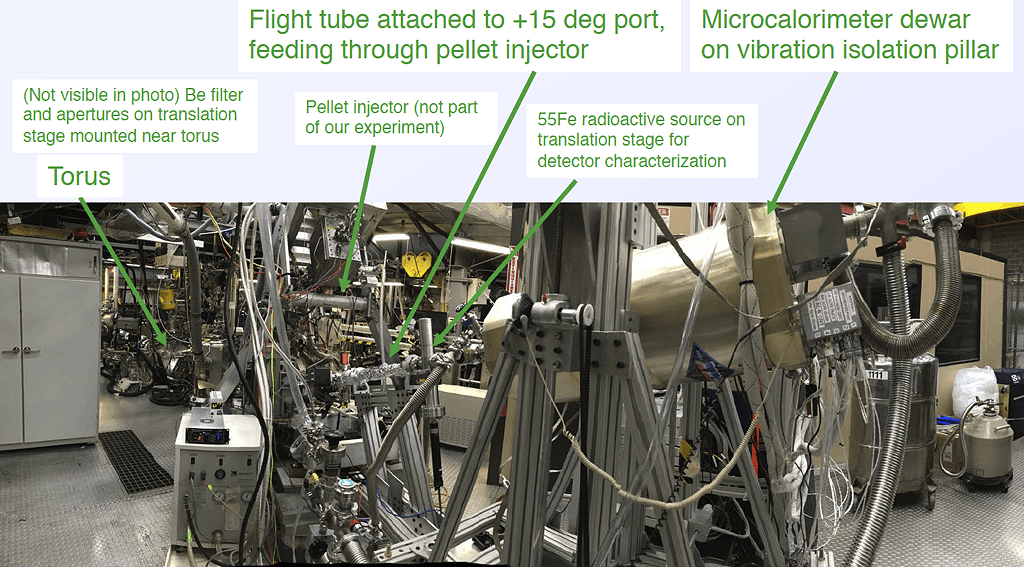
Microcalorimeter measurement of x-ray spectra from a high-temperature magnetically confined plasma
The LLNL/NASA x-ray microcalorimeter spectrometer installed on the MST facility has recorded x-ray photons emitted by aluminum impurity ions in a deuterium plasma. X-ray microcalorimeter development has been driven by space applications, where they have been used to make detailed measurements of astrophysical x-ray sources. The goal of this project is to adapt microcalorimeters for magnetic fusion energy research, and demonstrate the value of such measurements for fusion science. Microcalorimeter spectrometers combine the best characteristics of the x-ray instrumentation currently available on fusion devices: high spectral resolution similar to an x-ray crystal spectrometer, and the broadband coverage (0.1–12 keV) of an x-ray pulse height analysis system.
 This work was performed, in part, under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under Contract DE-AC52-07NA27344, based upon work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Fusion Energy Sciences.
This work was performed, in part, under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory under Contract DE-AC52-07NA27344, based upon work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science, Office of Fusion Energy Sciences.